
Your data is at risk every day. Threats include viruses, ransomware, natural disasters, hardware failure, and corruption, not to mention end-users losing documents or mistakenly deleting them. With all the possible ways your data can be lost, a single backup copy of your data is not enough to protect you. You need a rock-solid backup strategy to minimize the potential impact of these threats to your data integrity.
A good data backup strategy meets both your recovery time object (how long it takes to recover) and your recovery point objective (how old the backup data you restore will be). A good backup strategy also ensures that regardless of the type of incident, you are able to recover your original data.
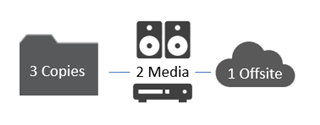
Quest highly recommends following the industry standard 3-2-1 backup strategy. A 3-2-1 strategy breaks down as the following:
- 3 copies of the data ( One live + two backups)
- 2 different medias used for the two backups
- 1 offsite copy
Let's look at how each of these items helps ensure the integrity of your data and how Rapid Recovery makes it easy to follow this strategy.
3 backup copies
The first copy of your production data, are the production files themselves. Your backup is creating a duplicate of those files allowing you to recover should the working copy become unusable. To mitigate risk, the 3-2-1 strategy dictates you should also retain a backup of your backup. This ensures that if your primary backup system becomes unusable also, you have a third copy of the files to recover from.
With Rapid Recovery there are 2 simple methods for ensuring that you have 3 copies of your data using either replication or archiving.
Replication - using Rapid Recovery replication you can send copies of your backups from one Core server to another. This allows a second server to contain the data hopefully at another physical location. There are a variety of options for setting up replication cores including using Cloud hosting like Microsoft Azure or Amazon AWS, using third party hosting services, or using your own secondary location in another data center or office location. By configuring replication you can ensure you have a live copy of your backup data offsite and available in case of a disaster. Don't forget that if you use replication you need to secure your Core servers to prevent ransomware from being able to jump from one Core server to another.
Archiving - using Rapid Recovery archiving you can schedule copies of your backups to be written to an archive location. Rapid Recovery supports direct archiving to a local disk (such as USB), a network location (CIFS share on the network somewhere), or to cloud storage such as Azure, Amazon, Google Cloud, Rackspace, or OpenStack. By scheduling regular archives you can ensure you have a copy of your data stored in a second location.
2 different medias
By using 2 different medias for backup storage, you can minimize the risk of hardware failure destroying your backups. Traditionally backup media has relied on disk and tape. However, with cloud storage so readily available and secure, cloud storage has become a common media used for storage of backups.
Rapid Recovery only supports disk based storage for the repository. This means that using replication to another Core server does not meet the 2 media requirement of this backup strategy. Hence you must use archiving. Cloud storage is the simplest method of including a second storage media since Rapid Recovery archives can be written directly to it and scheduled to run on regular intervals. If you wish to use tape as your second backup media, you must configure Rapid Recovery to write archives to a disk location (local or a CIFS share) and then use another backup software (such as Quest Netvault) to write the data to tape.
1 offsite copy
Having an offsite copy of all your backup data ensures that should you have a localized disaster, you will be able to recover from the backups stored in your secondary location. Either Rapid Recovery replication or archiving can provide this offsite copy functionality provided you configure your systems correctly. If using replication you should run your second core server offsite either in the cloud, at a third party hosting data center, or at a second location managed by your company. When using archiving, you should either use cloud archiving or archive to a media that can then be removed and stored offsite.
By following a 3-2-1 backup strategy you can mitigate many of the risks of data loss and ensure that you will always be able to recover from backup.



